What is Adrenal Insufficiency?
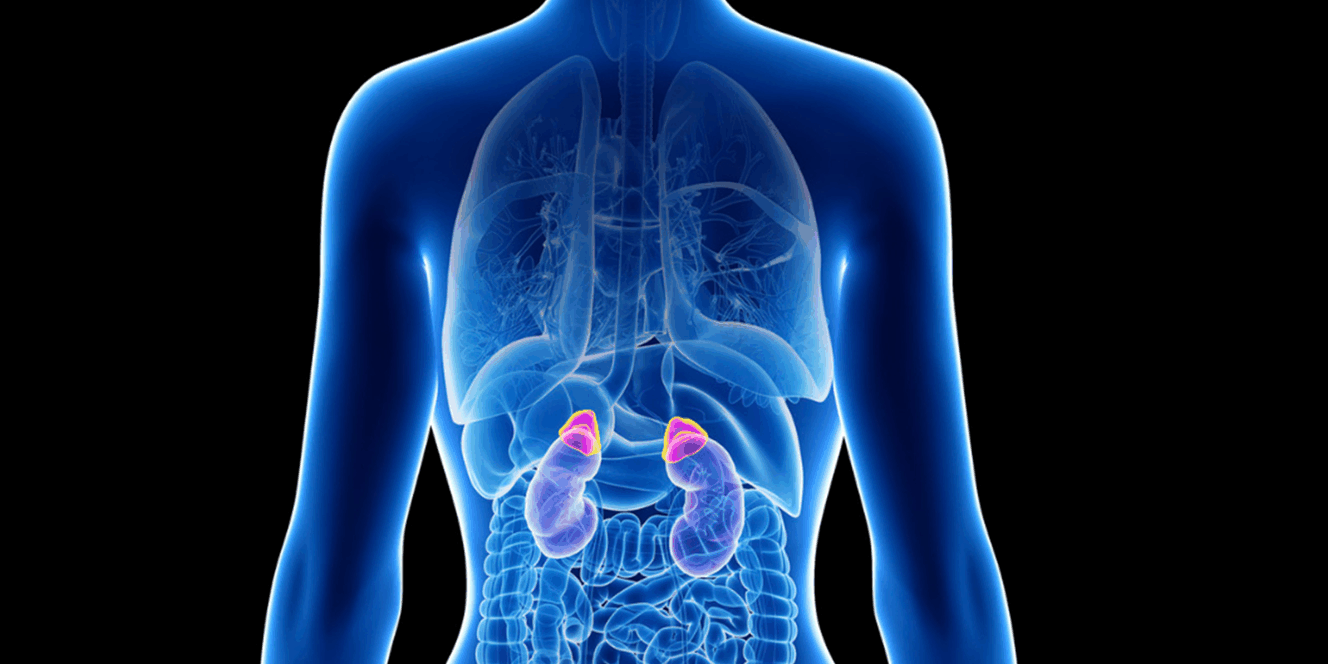
Adrenal Insufficiency is the condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones. The adrenal glands are two small glands located on top of the kidneys that regulate many important functions of the body. These glands produce the hormones necessary for the body to respond to stress. The main hormones secreted by the adrenal glands are cortisol, aldosterone and adrenaline.
Cortisol: A hormone that allows the body to cope with stress, regulates metabolism and controls the immune system.
Aldosterone: A hormone that regulates fluid and electrolyte balance.
Adrenaline: A hormone that quickly activates the body’s emergency response to danger.
Adrenal insufficiency is the condition in which these hormones are not produced enough and there are two main types:
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s Disease): It develops due to direct damage to the adrenal glands. This condition can be caused by the immune system attacking and destroying the adrenal glands. It is also known as Addison’s disease.
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency: It develops due to the pituitary gland not functioning properly. The pituitary gland sends a signal to the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, but when this signal is missing, the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol.
Adrenal Insufficiency is usually a slowly progressing disease that disrupts the body’s hormonal balance and can cause various physical and psychological symptoms. If not diagnosed early, adrenal insufficiency can lead to more serious health problems.
The main symptoms of adrenal insufficiency include fatigue, weight loss, low blood sugar, low blood pressure, excessive salt cravings, and brown spots on the skin. This disease causes the body to have difficulty performing its daily functions due to the lack of cortisol and other adrenal hormones in the body.
How to Understand Adrenal Insufficiency?
Adrenal insufficiency is usually caused by hormonal imbalances in the body, and symptoms can develop slowly over time. If this disease is not diagnosed correctly, it can lead to serious health problems in the body. Adrenal insufficiency reduces the body’s ability to cope with stress, resulting in a number of physical and psychological symptoms. Most of these symptoms are seen due to a deficiency of hormones produced by the adrenal glands.
The following symptoms should be considered to suspect adrenal insufficiency:
Excessive Fatigue and Weakness: One of the most common symptoms of adrenal insufficiency is extreme fatigue and weakness. The person may not feel rested even if they get enough sleep, and may have difficulty performing daily activities. This is due to low levels of the hormone cortisol, as cortisol is an important hormone that provides energy production and coping with stress.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Individuals with adrenal insufficiency may experience weight loss despite eating enough. The hormone cortisol regulates the body’s energy use, and when hormone levels are low, metabolism slows down, which can lead to weight loss.
Low Blood Pressure: Adrenal insufficiency leads to insufficient production of the hormone aldosterone, which regulates blood pressure by constricting blood vessels. This can result in dizziness, fainting, or low blood pressure. Symptoms such as dizziness, especially when standing, can be seen.
Constant Salt Cravings: Since adrenal insufficiency lacks the hormone aldosterone, which regulates salt balance in the body, people tend to consume salty foods. This indicates the body’s increased need for salt.
Skin Changes: In the case of Addison’s disease (primary adrenal insufficiency), brown spots or tanning may occur on the skin. This is due to increased melanin production. Brown spots can also appear in the mouth.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Adrenal insufficiency also affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Cortisol is a hormone that is necessary to raise blood sugar. When cortisol levels are low, a person can often experience low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and symptoms such as shaking, sweating, and dizziness may occur.
Depression and Anxiety: Low cortisol levels can disrupt the chemical balance in the brain. This can lead to depression, anxiety, and mood swings. These symptoms can be an important clue in diagnosing adrenal insufficiency.
Muscle and Joint Pain: Muscle weakness and joint pain are common in people with adrenal insufficiency. This occurs because the body’s ability to produce energy and heal is reduced.
Nausea and Vomiting: Adrenal insufficiency can also affect the digestive system. Digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite may occur.
Risk of Adrenal Crisis: Adrenal Insufficiency | If adrenal insufficiency is left untreated, it can become more serious over time and lead to a condition called “adrenal crisis.” An adrenal crisis is a life-threatening condition that develops suddenly and requires immediate intervention. Symptoms of an adrenal crisis include extreme weakness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, severe abdominal pain, and fever.
Adrenal insufficiency is usually diagnosed with blood tests. Cortisol and ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) levels can be measured to assess the function of the adrenal glands.
If you suspect adrenal insufficiency, it is very important to see a doctor, taking these symptoms into account. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the course of the disease and prevent complications.
What are the symptoms of adrenal crisis?
Adrenal Insufficiency | Adrenal crisis is one of the most serious and urgent conditions of adrenal insufficiency. When the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones, especially when cortisol levels drop too low, an adrenal crisis can develop. This means that the body completely loses its ability to cope with stress and serious health problems occur. Adrenal crisis is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate intervention.
Adrenal crisis symptoms usually develop rapidly and are severe. Understanding these symptoms is critical for timely intervention. Adrenal crisis symptoms can include:
Severe Fatigue and Weakness
Adrenal Insufficiency | During an adrenal crisis, a person experiences extreme fatigue and weakness. Although normally able to carry out daily activities, during an adrenal crisis, the person feels almost no energy and has difficulty getting out of bed.
Extremely Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Adrenal Insufficiency | Adrenal crisis can cause blood pressure to drop dangerously low. Low blood pressure (hypotension) can cause dizziness, fainting and loss of consciousness. Especially when standing, the person may be at risk of fainting.
Severe Abdominal Pain
Adrenal Insufficiency | Adrenal crisis can cause sudden and severe pain in the abdominal area. This pain can sometimes be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Abdominal pain can also be due to digestive problems caused by insufficient adrenal glands.
Nausea and Vomiting
Adrenal Insufficiency | During an adrenal crisis, the body reacts to the digestive system and the person often experiences nausea and vomiting. This can increase fluid loss and lead to dehydration (loss of fluid in the body), which makes the situation worse.
High Fever
Adrenal crisis can cause a high fever due to a severe infection or stress in the body. Fever usually occurs as a response to an emergency.
Rapid Breathing (Tachypnea) and Rapid Heartbeat (Tachycardia)
During an adrenal crisis, the body tries to take in oxygen quickly in order to survive. This causes an increase in breathing rate and an increase in heart rate. The person may have difficulty breathing and may experience a feeling of heart palpitations.
Loss of Consciousness and Restlessness
In a severe adrenal crisis, the person may lose consciousness. This can be seen especially in cases where blood pressure drops too low and not enough oxygen reaches the brain. In addition, the person may become restless during the crisis and their behavior may change dramatically.
Impairment of Brain Functions
Adrenal crisis can affect the normal functions of the brain. This can lead to confusion, loss of consciousness, depression and anxiety. A deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone can prevent the brain from functioning properly.
Severe Salt Cravings
People experiencing an adrenal crisis often have an extreme craving for salty foods. A deficiency of the hormone aldosterone disrupts the body’s salt and fluid balance, which can lead to a person craving salty foods.
Pale Skin and Cold Sweats
During an adrenal crisis, the skin may turn pale and sweating may begin as the body tries to maintain blood circulation. There may also be a feeling of coldness in the hands and feet.
Dehydration (Fluid Loss)
Vomiting, diarrhea, and sweating can cause dehydration, which can lead to fluid loss. In the event of an adrenal crisis, fluid loss in the body can occur very quickly and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Severe Dizziness or Fainting
An adrenal crisis can cause dizziness and fainting due to a sudden drop in blood pressure. This is especially noticeable when standing.
Adrenal Crisis Treatment
An adrenal crisis is a condition that requires immediate medical attention. Treatment is usually done with intravenous (IV) cortisol and fluid replacement. Early intervention can increase a person’s chance of survival. Cortisol treatment helps the body return to normal functions. In addition, fluid replacement is done to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
What Causes Adrenal Crisis?
Adrenal crisis can occur as a result of untreated adrenal insufficiency or situations that create excessive stress on the body (infections, surgical interventions, trauma, etc.). In addition, damage to the adrenal glands or sudden discontinuation of hormone therapy can also lead to adrenal crisis.
Adrenal crisis can be fatal if not treated in a timely manner. Therefore, it should be remembered that a person showing signs of adrenal insufficiency or adrenal crisis should receive immediate medical attention.
Can Adrenal Insufficiency Be Corrected?
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones, and this can be a lifelong disease that must be managed. However, depending on the type of adrenal insufficiency, treatment, and the patient’s overall health, the disease can be managed and symptoms can be controlled. Adrenal insufficiency is generally classified into two main types: primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease) and secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s Disease)
Primary adrenal insufficiency occurs when the adrenal glands are damaged or malfunctioning. In this case, the adrenal glands do not produce the cortisol, aldosterone, and other hormones that the body needs. This type of adrenal insufficiency is permanent, meaning that the adrenal glands do not fully recover. Addison’s disease can be caused by genetic factors, autoimmune diseases, infections, or other external factors.
Treatment:
Treatment for primary adrenal insufficiency usually requires lifelong hormone replacement therapy. Synthetic corticosteroids (prednisone, hydrocortisone) and aldosterone replacement (fludrocortisone) are used to replace cortisol. This treatment aims to correct the body’s hormone deficiencies and control the symptoms. With this type of treatment, most patients can live normal lives, but the disease is not completely “cured.” In other words, the disease is managed without the adrenal glands regaining their function.
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
Secondary adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce enough ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) and therefore fails to send signals to the adrenal glands. In this case, the adrenal glands are not stimulated to produce enough cortisol, leading to adrenal insufficiency. Secondary adrenal insufficiency usually develops as a result of long-term steroid therapy, but pituitary diseases can also cause it. Since the renin-angiotensin system is not affected, aldosterone production is usually preserved.
Treatment:
In the treatment of secondary adrenal insufficiency, hormone replacement is usually done. Cortisol treatment is used. If the pituitary gland is caused by a treatable problem, the function of the pituitary gland can be regained after treatment and the symptoms of adrenal insufficiency can be corrected. However, in patients with long-term steroid use or permanent pituitary gland damage, treatment can be lifelong.
Adrenal Insufficiency and Quality of Life
Although adrenal insufficiency is treated, patients may have to make some life changes. The lifestyle of these patients should be carefully managed to improve their physical and psychological health. Treatment for adrenal insufficiency usually includes the following:
Drug therapy: Hormone replacement therapy replaces the hormones produced by the adrenal glands. This treatment can be lifelong.
Stress management: People with adrenal insufficiency must learn to cope with stress. Because stress requires the adrenal glands to produce more cortisol, which can make patients’ health even more difficult.
Regular doctor check-ups: It is important for patients to go to their doctors regularly. Their hormone levels should be monitored regularly.
Balanced diet and fluid intake: People with adrenal insufficiency should pay attention to their salt consumption and drink enough fluids.
Can Adrenal Insufficiency Be Cured?
Although adrenal insufficiency is generally an incurable disease, patients’ quality of life can be significantly improved with treatment. Individuals with adrenal insufficiency who are treated can manage their symptoms and live a normal life. However, the natural function of the adrenal glands cannot be restored, meaning the disease is not completely cured. However, emergencies such as adrenal crisis can be prevented and patients can live a healthy life with treatment.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment in Adrenal Insufficiency
The earlier adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment can be. Therefore, it is important for people with symptoms of adrenal insufficiency to be evaluated by a specialist endocrinologist. Early diagnosis can help prevent adrenal crisis and other serious complications.
Adrenal insufficiency is a disease that can be controlled with treatment, but it is not possible to “cure” it completely. Treatment allows patients to manage their symptoms and live a healthy life. However, there is no current treatment to regain the natural function of the adrenal glands. Therefore, adrenal insufficiency requires a lifelong management process.
Diagnosis of Adrenal Insufficiency
Diagnosing adrenal insufficiency usually involves the following steps:
Clinical Evaluation: Adrenal Insufficiency | The first step is to thoroughly review the patient’s symptoms and perform a physical exam. This includes fatigue, weakness, muscle weakness, weight loss, and other symptoms.
Laboratory Tests: Adrenal Insufficiency | Blood tests are performed to measure cortisol levels. In addition, an ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) test may be used. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, and irregularities in its levels can help diagnose adrenal insufficiency.
Advanced Tests: Adrenal Insufficiency | If initial tests are insufficient to confirm a diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency, more advanced tests such as an ACTH stimulation test or insulin tolerance test may be performed.
Treatment of Adrenal Insufficiency
Hormone Replacement
The basis of treatment for adrenal insufficiency is to supplement the body with the deficient hormones. The cortisol hormone is usually given in the form of oral tablets, but in some cases, IV drugs or injections may also be required. Hormone levels should be carefully monitored during the treatment process.
Lifestyle Changes
Stress management, regular exercise, healthy nutrition and sleep patterns can help support adrenal functions. In particular, it can be supported with the nutrients and supplements the body needs in terms of nutrition.
Psycho-Social Support and Stress Management
Adrenal insufficiency can affect the person psychologically as well as physically. Psychological problems such as depression, anxiety and anxiety may develop due to adrenal insufficiency, so it is important to address such problems with professional support.
Adrenal Insufficiency and Monitoring of Patients
Adrenal Insufficiency treatment is a process that requires constant monitoring and regular follow-up. During the treatment process, the patients’ condition should be evaluated at regular intervals and drug doses should be adjusted. In acute infection cases, patients are informed about increasing the current drug doses.
Adrenal Insufficiency | In addition, appropriate training is given to patients for emergency situations such as adrenal crisis and emergency treatment protocols are created when necessary. This allows patients to more safely progress through the adrenal insufficiency treatment process.